Can Early Detection of Gastrointestinal Disorders Preserve Physical and Mental Health?
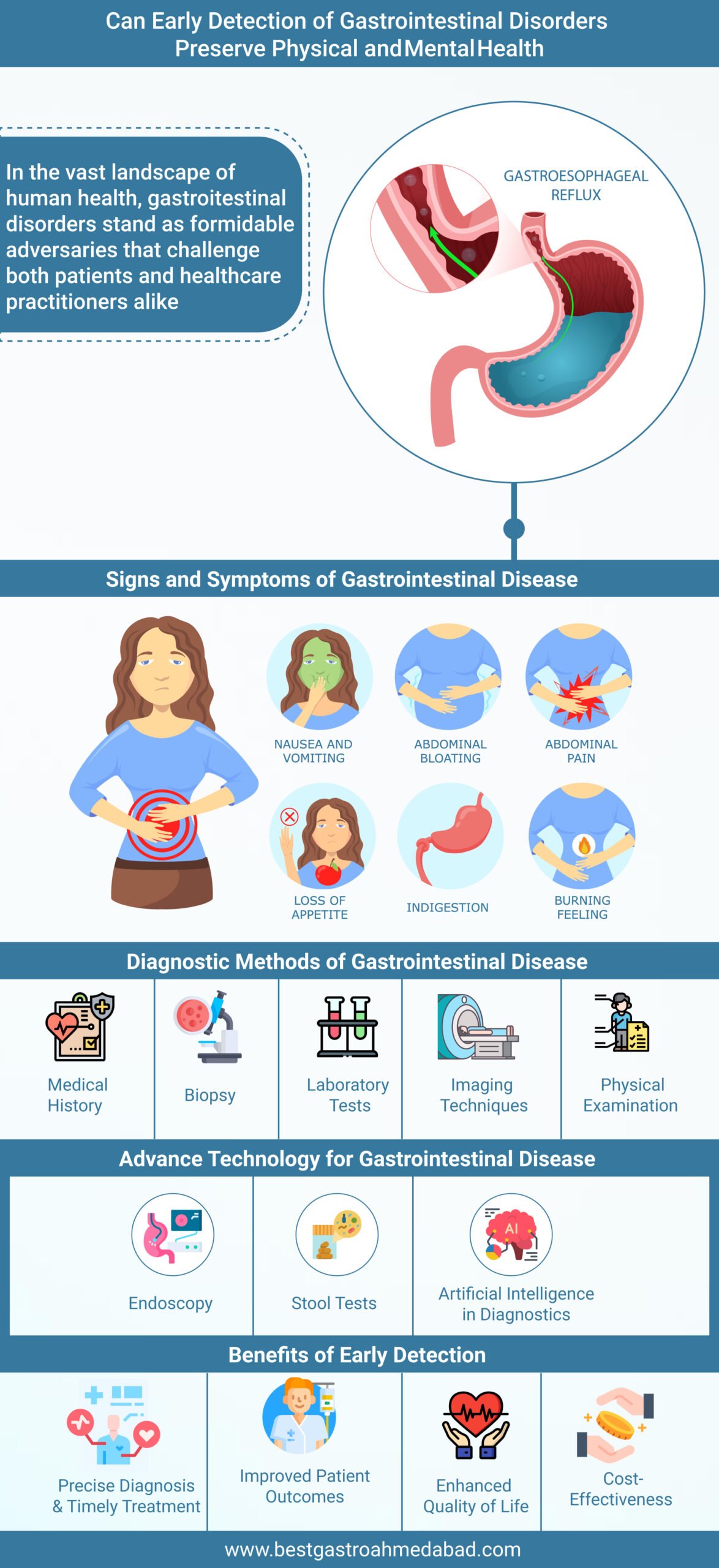
In the vast landscape of human health, gastrointestinal disorders stand as formidable adversaries that challenge both patients and healthcare practitioners alike. Among these enigmatic foes, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), Crohn’s disease, and ulcers reign as silent tormentors, influencing the quality of life for many. Delving into their prevalence, impact, and the pressing need for early detection to stave off further complications, we venture into the scientific abyss of gastrointestinal disorders.
Recognizing Warning Signs and Symptoms of gastrointestinal disease
Abdominal Discomfort
- Persistent Abdominal Pain: Chronic and unexplained pain in the abdomen could signal an underlying gastrointestinal issue.
- Cramping: Frequent and intense abdominal cramps may be indicative of gastrointestinal distress.
Bowel Habits
- Altered Bowel Movements: Sudden changes, like recurring diarrhea, constipation, or alternating between both, warrant attention.
- Unexplained Bleeding: Presence of blood in the stool requires immediate investigation.
Digestive Discomfort
- Bloating: Unrelenting abdominal bloating and distension may signify gastrointestinal dysfunction.
- Flatulence: Excessive gas and frequent passing could indicate gastrointestinal disturbances.
Lingering Discomfort and Fatigue
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Gradual and unexplained weight loss may be linked to gastrointestinal disorders.
- Fatigue: Persistent and unexplained fatigue may be a symptom worth investigating.
Embracing Proactivity for Gut Health
- Listen to Your Body Pay attention to your body’s cues and any abnormal gastrointestinal signals for early detection.
- Nourish Your Gut Adopt a diet rich in fiber, probiotics, and wholesome nutrients to promote gut health.
- Seek Professional Guidance Consult healthcare professionals if gastrointestinal symptoms persist or worsen.
Unravelling Gastrointestinal Mysteries: Diagnostic Methods Explored
In the pursuit of uncovering gastrointestinal issues, healthcare professionals employ a range of diagnostic methods, harnessing the power of medical technology to delve into the depths of the human digestive system. From traditional techniques to cutting-edge advancements, these tools play a vital role in early detection, timely intervention, and improved patient outcomes.
Medical History and Physical Examination
- The initial step involves a comprehensive review of the patient’s medical history and a thorough physical examination to identify potential gastrointestinal disorders symptoms and risk factors.
Laboratory Tests
- Blood Tests: Assessing blood samples aids in detecting abnormalities, inflammation, or signs of infection in the gastrointestinal system.
- Stool Tests: Examination of stool samples can reveal hidden blood, pathogens, or markers of gastrointestinal disorders.
Imaging Techniques
Endoscopy: A versatile tool, endoscopy involves inserting a flexible tube with a camera (endoscope) into the digestive tract to visualize the esophagus, stomach, and intestines. Different types include: –
- Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD): Examines the upper gastrointestinal tract.
- Colonoscopy: Is used to examine the path of colon
- Capsule Endoscopy: A small, swallowable camera capsule captures images as it moves through the gastrointestinal tract.
- CT Scan and MRI: Cross-sectional imaging techniques that provide detailed images of the gastrointestinal organs and surrounding tissues.
Biopsy
- During endoscopy or other procedures, tissue samples (biopsies) may be taken for further analysis to confirm specific gastrointestinal conditions.
Advancements in Medical Technology: Pioneering the Way
Endoscopies
- Modern endoscopes offer enhanced visualization with high-definition imaging, enabling better detection of abnormalities.
- Advanced endoscopic techniques, such as endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) and endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP), enable precise diagnosis and therapeutic interventions.
Stool Tests
- Rapid advances in stool test technology allow for more accurate and sensitive detection of gastrointestinal infections and markers of disease.
Artificial Intelligence in Diagnostics
- AI-driven diagnostic tools can analyze vast amounts of patient data, assisting healthcare professionals in early detection and accurate diagnosis.
- AI algorithms applied to imaging studies can aid in identifying potential abnormalities and flagging areas of concern.
Benefits of Early Detection: Empowering Timely Intervention
Precise Diagnosis and Timely Treatment
- Early detection facilitates prompt diagnosis, enabling timely implementation of appropriate treatment strategies.
- It minimizes delays in addressing potential complications and managing symptoms effectively.
Improved Patient Outcomes
- Early intervention enhances the likelihood of successful treatment outcomes and improved overall patient health.
- Preventive measures can be initiated to reduce the risk of disease progression and complications.
Enhanced Quality of Life
- Early detection and subsequent management of gastrointestinal issues alleviate symptoms, leading to a better quality of life for patients.
Cost-Effectiveness
- Timely intervention can potentially reduce the need for complex and costly procedures, leading to overall cost savings in healthcare.
Unravelling the Gut-Brain Axis: A Nexus of Communication
In the uncharted territory of the gut-brain axis, emerging research sheds light on the intricate connection between the gut and mental health, illuminating a path that intertwines the physical and the psychological. Within this symbiotic relationship lies a revelation: gastrointestinal disorders possess the capacity to mold and manipulate mental well-being, leaving a profound impact on conditions like anxiety and depression. Let us embark on an expedition of knowledge, traversing the realms of scientific discovery, as we explore the profound implications of this connection and the potential for early detection and treatment to transform lives.
- The Gut’s Hidden Influence: The gut-brain axis acts as a bidirectional communication pathway, connecting the central nervous system and the gut’s intricate network of neurons, known as the enteric nervous system.
- Neurotransmitters and Beyond: Chemical messengers, including serotonin, dopamine, and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), play pivotal roles in mediating this cross-talk, influencing both emotional and gastrointestinal responses.
Gastrointestinal Disorders: Catalysts of Mental Health Disarray
Anxiety and Gastrointestinal Disorders
- The Stress Connection: Chronic gastrointestinal distress can elevate stress hormones, intensifying anxiety symptoms.
- Gut Microbiome Impact: Imbalances in the gut microbiome, observed in gastrointestinal disorders, may contribute to anxiety through the gut-brain axis.
Depression and Gastrointestinal Disorders
- Shared Inflammation: Gastrointestinal disorders often involve inflammation, which may trigger or worsen depressive symptoms.
- Altered Neurotransmitter Levels: Imbalances in neurotransmitters caused by gastrointestinal disorders can contribute to mood disturbances.
A Beacon of Hope: Early Detection and Treatment
Identifying Warning Signs
- Gastrointestinal disorders and mental health conditions share common symptoms, emphasizing the importance of vigilance and thorough evaluation.
- Key indicators include unexplained abdominal pain, digestive disturbances, mood fluctuations, and changes in appetite or weight.
A Holistic Approach to Care
- Integrative healthcare practices recognize the gut-brain axis and adopt holistic treatment strategies, addressing both physical and mental well-being.
- Collaboration between gastroenterologists and mental health professionals ensures comprehensive care.
Therapeutic Interventions
- Lifestyle Modifications: Dietary changes, stress management techniques, and regular exercise can positively impact both gastrointestinal health and mental well-being.
- Medication: Targeted medications for gastrointestinal disorders and mental health conditions can alleviate symptoms and improve overall functioning.
Psychotherapy and Mindfulness
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and other psychotherapies can assist patients in coping with the challenges of gastrointestinal disorders and managing associated mental health symptoms.
- Mindfulness practices offer tools to reduce stress and cultivate a balanced mind-body connection.
Embracing a Healthier Horizon: Physical and Mental Wellness Aligned
- Advancing Research: Continued investigation into the gut-brain axis will offer insights into novel therapeutic approaches and personalized treatment options.
- Empowering Lives: Early detection and targeted treatment have the potential to mitigate the toll of gastrointestinal disorders on mental health, leading to improved overall well-being.
- Nurturing Hope: Emphasizing the interplay between gastrointestinal health and mental well-being encourages proactive measures and destigmatizes mental health concerns.
Conclusion
Amidst the intricate world of gastrointestinal disorders, a profound connection emerges, revealing how these ailments can reverberate beyond the gut, influencing both physical and mental well-being. The subtle symptoms of gastrointestinal disease hold untold significance, for they may herald the onset or exacerbation of anxiety and depression. Understanding the warning signs becomes crucial as we journey through this landscape, guided by the wisdom of Dr. Vatsal Mehta. By embracing early detection and tailored treatment, we can forge a path towards improved overall health, addressing both the complexities of gastrointestinal disorders and the shadows they cast upon mental wellness.